Medical device compliance is essential to ensure that each product is safe and effective for its intended use. It encompasses various aspects, including regulatory, clinical and technical, ensuring that the device complies with current legal and normative requirements.
European standards and regulations
Initially, the medical device manufacturer must meet the general requirements of the European Union regulation (2017/745). There are in fact several standards that are adapted to each type of medical device, but there is a list of harmonized standards that are most often used by manufacturers. One example is EN ISO 13485, which sets out the requirements for a quality management system. Today, regulatory bodies play a very important role in monitoring and approving devices before they are placed on the market. Appointed by a member state of the European Union, these notified bodies are responsible for assessing devices to ensure their safety and full compliance with requirements, and then issuing the CE mark.

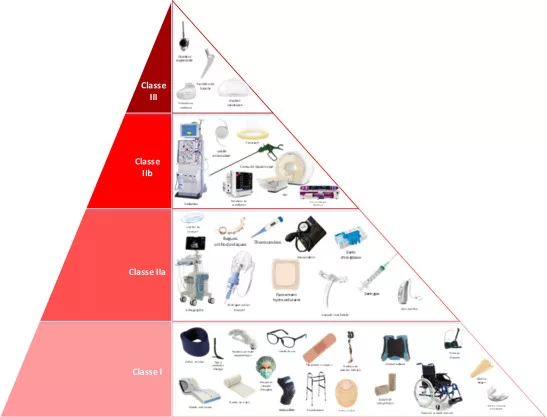
The different compliance classes and levels
Medical devices (MDs) are classified into different categories according to their complexity, use and risk to patients and users. Their classification generally follows the framework defined by the European Union, which comprises four classes:
– Class I for low-risk medical devices, such as corrective spectacles
– Class IIa and IIb for medical devices of moderate to high risk, such as contact lenses (IIa) and respirators (IIb).
– Class III for high-risk medical devices, such as artificial hearts.
In terms of compliance, Class I is simplified by the low risk involved, requiring only self-declaration and basic monitoring.
Class II and above may require clinical trials, more demanding documentation and assessment by notified bodies.
Finally, for Class III, extensive pre-clinical and clinical trials are mandatory, with particularly detailed documentation and more rigorous assessment by certified bodies. Strict, ongoing post-marketing monitoring is also required.
These different approaches put into perspective the higher costs and lead times incurred by Class III devices.

Key stages in the compliance process for a total artificial heart
The compliance process for a medical device as complex as a total artificial heart involves several rigorous stages to guarantee its safety and efficacy before, during and after it is brought to market.
The first stage is research and development (R&D), which begins by conceptualizing the device and defining its technical and functional specifications. Prototype design incorporates regulatory requirements from the outset.
Next come preclinical studies. In vitro tests are carried out to assess the materials used, their biocompatibility and durability. These are followed by in vivo tests on animals to verify the prototype’s performance and safety under real-life biological conditions.
Once these tests have been successfully completed, the documentation and data compilation phase begins, to produce a complete and detailed dossier.
Next come the clinical trials (on humans), which are divided into several phases: initial tests on a small group of patients to assess basic safety, then a larger group to assess efficacy and adjust technical parameters, and finally large-scale clinical trials to confirm safety and efficacy.
Once the clinical trials have been completed, the complete technical file is submitted to a notified body for assessment. Once certified, the artificial heart enters the large-scale production phase, in compliance with quality and distribution standards.

Procope Medicals is now entering the pre-clinical studies phase, with the aim of carrying out these tests over the next 24 months. This phase begins with a rigorous action plan to meet the regulatory requirements for its medical device.
Sources :
https://www.snitem.fr/le-dispositif-medical-dm/dm-et-cadre-reglementaire/la-reglementation-des-dispositifs-medicaux/#:~:text=La réglementation qui encadre le,sur le marché des DM.
https://lne-gmed.com/fr/notified-bodies-role#:~:text=Un organisme notifié est un,à disposition des dispositifs médicaux.
